Friday, 28 June 2013
Insight State management
softMind IT Tutorial: Maintaining Session in MVC
In ASP.net we used following state management tricks. Ofcourse not all but of the tricks we can still use in MVC build applications.
Client-Based State Management Options
- View State -- NOT IN MVC
- Control State -- NOT IN MVC
- Hidden Fields
- Cookies
- Query Strings
Server-Based State Management Options
- Application State
- Profile Properties
- Session State
Levels of state management :
- Single or multiple page level: State management at single as well as multiple page level i.e., managing state between page requests.
- User level: State should be preserved as long as a user is running the application.
- Application level: State available for complete application irrespective of the user, i.e., should be available to all users.
- Application to application level: State management between or among two or more applications
Session is maintained in MVC using :
- Tempdata
- viewdata
- viewbag
Insight Properties in C#
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In C#, properties are nothing but natural extension of data fields. They are usually known as 'smart fields' in C# community.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In C#, properties are nothing but natural extension of data fields. They are usually known as 'smart fields' in C# community.
The general form of declaring a property is as follows.
<acces_modifier> <return_type> <property_name>
private int myVar;
public int MyProperty
{
get { return myVar; }
set { myVar = value; }
}
Since normal data fields and properties are stored in the same memory space, in C#, it is not possible to declare a field and property with the same name.
Why we use properties.
There could be the confusion why we prefer properties when we can public fields instead.
there are many reasons some of them are as follows.
1) properties allow for more error checking, among other things.
public Color Color{get {return _Color;}set{ if (value == Color.LimeGreen) throw new Exception("That is a rediculous color.");_Color = value;}2)properties are more flexible than fields in that you can have read only properties, write only properties3)properties that don't necessarily map to a single private field etc.4) properties help in triggering events on change of values of object membersbool started; public bool Started { get { return started; } set { started = value; if (started) OnStarted(EventArgs.Empty); } }Interesting thing to know is that you can use methods just like properties although methods are generally about actions/behaviour and properties are about an objects data and hence its easier to catch at data level than at actions or behaviour level.
Insight Cluster Index and Non Cluster Index
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Think about a table, say
For learning..
STEP 1:
CREATE TABLE Student(StudId smallint, StudName varchar(50), Class tinyint);
CREATE TABLE TotalMarks(StudentId smallint, TotalMarks smallint);
Go
STEP 2:
We will mark the
Clustered Index
Now let us assume that we had written a query like below:
Select * from student where studid = 103;
Select * from student where studid = 107;
Execution WITHOUT index --
First search will return data at Fourth comparison.
Second search will return data at 8th comparison.
Execution WITH index --
First search will return data at 1st comparison.
Second search will return data at 3rd comparison.
Non Clustered Index::
A non-clustered index is useful for columns that have some repeated values. Say for example,
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Think about a table, say
Customer (For any leading bank India), that has around 16 million records. When we try to retrieve records for two or three customers based on their customer id, all 16 million records are taken and comparison is made to get a match on the supplied customer ids. Think about how much time that will take if it is a web application and there are 25 to 30 customers that want to access their data through internet. Does the database server do 16 million x 30 searches? The answer is no because all modern databases use the concept of index.Index is a database object, which can be created on one or more columns (16 Max column combination). When creating the index will read the column(s) and forms a relevant data structure to minimize the number of data comparisons. The index will improve the performance of data retrieval and adds some overhead on data modification such as create, delete and modify. So it depends on how much data retrieval can be performed on table versus how much of DML (Insert, Delete and Update) operations.For learning..
STEP 1:
CREATE TABLE Student(StudId smallint, StudName varchar(50), Class tinyint);
CREATE TABLE TotalMarks(StudentId smallint, TotalMarks smallint);
Go
STEP 2:
We will mark the
StudId column of the Student table as primary key.Clustered Index
The primary key created for the
StudId column will create a clustered index for the Studid column. A table can have only one clustered index on it.
When creating the clustered index, SQL server 2005 reads the
Studid column and forms a Binary tree on it. This binary tree information is then stored separately in the disc. Expand the table Student and then expand the Indexes. You will see the following index created for you when the primary key is created:
With the use of the binary tree, now the search for the student based on the
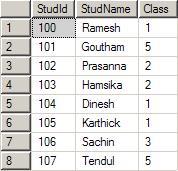
studid decreases the number of comparisons to a large amount. Let us assume that you had entered the following data in the table student:
The
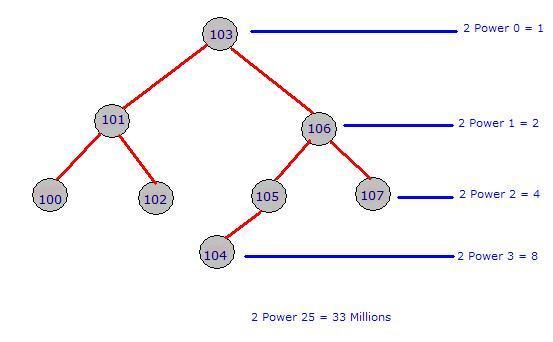
index will form the below specified binary tree. Note that for a given parent, there are only one or two Childs. The left side will always have a lesser value and the right side will always have a greater value when compared to parent. The tree can be constructed in the reverse way also. That is, left side higher and right side lower.Now let us assume that we had written a query like below:
Select * from student where studid = 103;
Select * from student where studid = 107;
Execution WITHOUT index --
First search will return data at Fourth comparison.
Second search will return data at 8th comparison.
Execution WITH index --
First search will return data at 1st comparison.
Second search will return data at 3rd comparison.
Non Clustered Index::
A non-clustered index is useful for columns that have some repeated values. Say for example,
AccountType column of a bank database may have 10 million rows. But, the distinct values of account type may be 10-15. A clustered index is automatically created when we create the primary key for the table. We need to take care of the creation of the non-clustered index.
Follow the steps below to create a Non-clustered index on our table
Student based on the column class.- After expanding the
Studenttable, right click on theIndexes. And click on the New Index.
- From the displayed dialog, type the index name as shown below and then click on the Add button to select the column(s) that participate in the index. Make sure the
Indextype is Non-Clustered.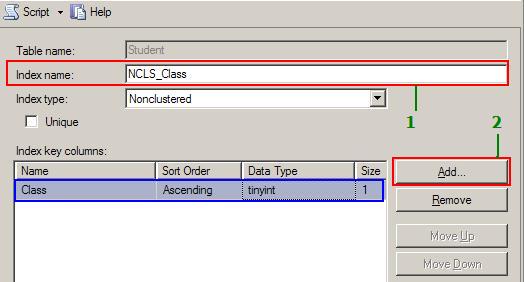
- In the select column dialog, place a check mark for the column class. This tells that we need a non-clustered index for the column
Student.Class. You can also combine more than one column to create theIndex. Once the column is selected, click on the OK button. You will return the dialog shown above with the selected column marked in blue. Our index has only one column. If you selected more than one column, using theMoveUpandMoveDownbutton, you can change order of the indexed columns. When you are using the combination of columns, always use the highly repeated column first and more unique columns down in the list. For example, let use assume the correct order for creating the Non-clustered index is:Class,DateOfBirth,PlaceOfBirth.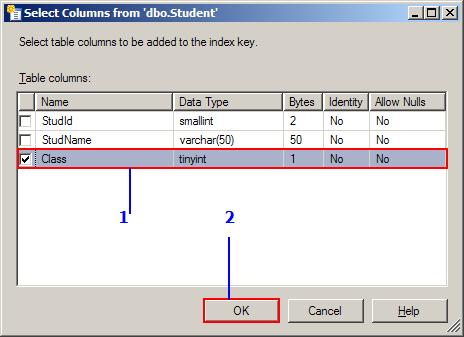
- Click on the Index folder on the right side and you will see the non-clustered index based on the column class is created for you.
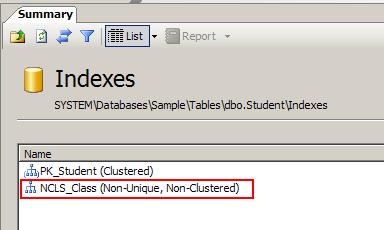
A table can have more than one Non-Clustered index. But, it should have only one clustered index that works based on the Binary tree concept. Non-Clustered column always depends on the Clustered column on the database.
=============================
A clustered index is a special type of index that reorders the way records in the table are physically stored. Therefore table can have only one clustered index. The leaf nodes of a clustered index contain the data pages. A nonclustered index is a special type of index in which the logical order of the index does not match the physical stored order of the rows on disk. The leaf node of a nonclustered index does not consist of the data pages. Instead, the leaf nodes contain index rows.
With a non clustered index there is a second list that has pointers to the physical rows. You can have many non clustered indexes, although each new index will increase the time it takes to write new records.
================================
=============================
A clustered index is a special type of index that reorders the way records in the table are physically stored. Therefore table can have only one clustered index. The leaf nodes of a clustered index contain the data pages. A nonclustered index is a special type of index in which the logical order of the index does not match the physical stored order of the rows on disk. The leaf node of a nonclustered index does not consist of the data pages. Instead, the leaf nodes contain index rows.
With a non clustered index there is a second list that has pointers to the physical rows. You can have many non clustered indexes, although each new index will increase the time it takes to write new records.
================================
Working of non-cluster index,
This can be easily explained with the concept of a book and its index page at the end. Let us assume that you are going to a bookshop and found a big 1500 pages of C# book that says all about C#. When you glanced at the book, it has all beautiful color pages and shiny papers. But, that is not only the eligibility for a good book right? One you are impressed, you want to see your favorite topic of Regular Expressions and how it is explained in the book. What will you do? I just peeped at you from behind and recorded what you did as below:
This can be easily explained with the concept of a book and its index page at the end. Let us assume that you are going to a bookshop and found a big 1500 pages of C# book that says all about C#. When you glanced at the book, it has all beautiful color pages and shiny papers. But, that is not only the eligibility for a good book right? One you are impressed, you want to see your favorite topic of Regular Expressions and how it is explained in the book. What will you do? I just peeped at you from behind and recorded what you did as below:
- You went to the Index page (it has total 25 pages). It is already sorted and hence you easily picked up Regular Expression that comes on page Number 17.
- Next, you noted down the number displayed next to it which is 407, 816, 1200-1220.
- Your first target is Page 407. You opened a page in the middle, the page is greater than 500.
- Then you moved to a somewhat lower page. But it still reads 310.
- Then you moved to a higher page. You are very lucky you exactly got page 407. [Yes man you got it. Otherwise I need to write more. OK?]
- That’s all, you started exploring what is written about Regular expression on that page, keeping in mind that you need to find page 816 also.
In the above scenario, the Index page is Non-Clustered index and the page numbers are clustered index arranged in a binary tree. See how you came to the page 407 very quickly. Your mind actually traversed the binary tree way left and right to reach the page 407 quickly.
Thursday, 27 June 2013
Insight Caching
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Introduction: Caching enables you to store data in memory for rapid access. When the data is accessed again, applications can get the data from the cache instead of retrieving it from the original source. This can improve performance and scalability. In addition, caching makes data available when the data source is temporarily unavailable.Larger number of client means larger number of requests to your web server and heavy load on the network causing performance issue. For solving this problem, I worked on using caching on our web application.
What is Caching?
web site can have a heavy load on the site which can increase exponentially, which can slow down the server as well as the access of the site. Slow access is the most common problem for web sites when accessed by a large number of clients simultaneously. For resolving this problem, we can use a high level of hardware configuration, load balancer, high bandwidth, but load is not the only reason that makes a website slow, so we need to provide a kind of mechanism which will also provide fast data access and provide performance improvements. Caching provides the solution.Caching is a technique where we can store frequently used data, and web pages are stored temporarily on the local hard disk for later retrieval. This technique improves the access time when multiple users access a web site simultaneously, or a single user accesses a web site multiple times. Caching for web applications can occur on the client (browser caching), on a server between the client and the web server, (proxy caching / reverse proxy caching), and on the web server itself (page caching or data caching).
Thus in total we have three type of caching
1)Browser caching -- Caching for web applications can occur on the client.
2) Proxy caching/ reverse proxy caching -- on a server between the client and the web server.
3) Page caching/ data caching -- on the web server itself.
1. Client Caching: In Client Caching, the client browser performs caching by storing cached data on the local disk as a temporary file or in the browser internal memory. This provides quick access of some information which reduces the network load and the server load also. This information can't be shared by other clients so it is client specific.
2. Proxy Caching: The main disadvantage of client caching is data that is stored on the client browser is client specific. Proxy caching uses a dedicated server that stores caching information in between the client and the web server in a shared location so that all clients can use the same shared data. The proxy server (e.g., Microsoft Proxy Server) fulfills all the requests for the web page without sending out the request to the actual web server over the internet, resulting in faster access.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Introduction: Caching enables you to store data in memory for rapid access. When the data is accessed again, applications can get the data from the cache instead of retrieving it from the original source. This can improve performance and scalability. In addition, caching makes data available when the data source is temporarily unavailable.Larger number of client means larger number of requests to your web server and heavy load on the network causing performance issue. For solving this problem, I worked on using caching on our web application.
What is Caching?
web site can have a heavy load on the site which can increase exponentially, which can slow down the server as well as the access of the site. Slow access is the most common problem for web sites when accessed by a large number of clients simultaneously. For resolving this problem, we can use a high level of hardware configuration, load balancer, high bandwidth, but load is not the only reason that makes a website slow, so we need to provide a kind of mechanism which will also provide fast data access and provide performance improvements. Caching provides the solution.Caching is a technique where we can store frequently used data, and web pages are stored temporarily on the local hard disk for later retrieval. This technique improves the access time when multiple users access a web site simultaneously, or a single user accesses a web site multiple times. Caching for web applications can occur on the client (browser caching), on a server between the client and the web server, (proxy caching / reverse proxy caching), and on the web server itself (page caching or data caching).
Thus in total we have three type of caching
1)Browser caching -- Caching for web applications can occur on the client.
2) Proxy caching/ reverse proxy caching -- on a server between the client and the web server.
3) Page caching/ data caching -- on the web server itself.
1. Client Caching: In Client Caching, the client browser performs caching by storing cached data on the local disk as a temporary file or in the browser internal memory. This provides quick access of some information which reduces the network load and the server load also. This information can't be shared by other clients so it is client specific.
2. Proxy Caching: The main disadvantage of client caching is data that is stored on the client browser is client specific. Proxy caching uses a dedicated server that stores caching information in between the client and the web server in a shared location so that all clients can use the same shared data. The proxy server (e.g., Microsoft Proxy Server) fulfills all the requests for the web page without sending out the request to the actual web server over the internet, resulting in faster access.
Proxy caches are often located near network gateways to reduce bandwidth usage. Some times multiple proxy cache servers are used for larger number of clients. This is called a cache array.
4. Web Server Caching: In web server caching, cached data is stored inside the web server. Data caching and pagecaching uses the web sever caching mechanism.
Advantages of Caching
1) reduced network traffic
2) Reduces bandwidth consumption.
3) Reduces server overload.
4) Reduces time take to download information.
5) Can also used to reduced round trips to database server.
Caching in .NET
ASP.NET provides support for page, partial page (fragment), and data caching.
ASP.NET supports three types of caching:
- Page output caching [Output caching]
- Fragment caching [Output caching]
- Data caching
In the picture, when the first request is generated, the page is cached and for the same page request in future, the page is retrieved from the cache rather that regenerating the page.
For output caching, an
OutputCache directive can be added to any ASP.NET page, specifying the duration (in seconds) that the page should be cached.Output caching location
As I have already mentioned, we can store cached data in different locations like client, server, or in between the client and the server. Now I am going to discuss how to set the location of cached data. If we store cached data, it saves the page rendering time by fetching data from the cache. There is another way that we can save cached data on the client browser, which reduces network traffic. The
OutputCache directive on a page enables all three types of caching—server, client, and proxy—by default.
2. Page Fragment Caching
<!— UserControl.ascx —>
<%@ OutputCache Duration='60'
VaryByParam='none' %>
<%@ Control Language="'C#'" %>
<script runat="server">
protected void Page_Load(Object src, EventArgs e)
{
_date.Text = "User control generated at " +
DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
</script>
<asp:Label id='_date' runat="'server'" />
Here I have user caching on a user control, so whenever we use it in a page, part of the page will be cached.
3. Data Caching: Caching data can dramatically improve the performance of an application by reducing database contention and round-trips. Simply, data caching stores the required data in cache so that the web server will not send requests to the DB server every time for each and every request, which increases web site performance. For datacaching, we need to cache data which is accessible to all or which is very common. The data cache is a full-featured cache engine that enables you to store and retrieve data between multiple HTTP requests and multiple sessions within the same application.
Now let us see how we can implement data caching in our web application. There are three different ways to add data or objects into cache. But based on the situation, we have to access it differently. These methods are
Cache[],Cache.add(), cache.insert(). The following table will show you the clear difference of the there methods.Wednesday, 26 June 2013
Insight Finally
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
the finally block is reached immediately after processing completes. In this way, the finally block can be used to ensure that some logic is always executed before the method is exited.The finally block is useful for cleaning up any resources allocated in the try block. Control is always passed to the finally block regardless of how the try block exits. This statement takes the following form.Whereas catch is used to handle exceptions that occur in a statement block, finally is used to guarantee a statement block of code executes regardless of how the preceding try block is exited.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
the finally block is reached immediately after processing completes. In this way, the finally block can be used to ensure that some logic is always executed before the method is exited.The finally block is useful for cleaning up any resources allocated in the try block. Control is always passed to the finally block regardless of how the try block exits. This statement takes the following form.Whereas catch is used to handle exceptions that occur in a statement block, finally is used to guarantee a statement block of code executes regardless of how the preceding try block is exited.
Insight Collections
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Collection classes serve various purposes, such as allocating memory dynamically to elements and accessing a list of items on the basis of an index etc. These classes create collections of objects of the Object class, which is the base class for all data types in C#.Collections are enhancement to the arrays.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Collection classes serve various purposes, such as allocating memory dynamically to elements and accessing a list of items on the basis of an index etc. These classes create collections of objects of the Object class, which is the base class for all data types in C#.Collections are enhancement to the arrays.
There are two distinct collection types in C#. The standard collections, which are found under the System.Collections namespace and the generic collections, under System.Collections.Generic. The generic collections are more flexible and are the preferred way to work with data. The generic collections or generics were introduced in .NET framework 2.0. Generics enhance code reuse, type safety, and performance.
various commonly used classes of the System.Collection namespace
ArrayList
Hashtable
SortedList
Stack
Queue
BitArray
LIST
dictionary
ArrayList--It represents ordered collection of an object that can be indexed individually. It is basically an alternative to an array. However unlike array you can add and remove items from a list at a specified position using an index and the array resizes itself automatically. It also allows dynamic memory allocation, add, search and sort items in the list
Hashtable--It uses a key to access the elements in the collection.A hash table is used when you need to access elements by using key, and you can identify a useful key value. Each item in the hash table has a key/value pair. The key is used to access the items in the collection.
BitArray--It represents an array of the binary representation using the values 1 and 0.It is used when you need to store the bits but do not know the number of bits in advance. You can access items from the BitArray collection by using an integer index, which starts from zero.
LIST--A
List is a strongly typed list of objects that can be accessed by index. It can be found under System.Collections.Generic namespace.
dictionary--A dictionary, also called an associative array, is a collection of unique keys and a collection of values, where each key is associated with one value. Retrieving and adding values is very fast. Dictionaries take more memory, because for each value there is also a key.
Dictionary<string, string> domains = new Dictionary<string, string>();
domains.Add("de", "Germany");
Non-Generic collections - These are the collections that can hold elements of different data types. It holds all elements as object type.
So it includes overhead of type conversions.
Generic collections - These are the collections that can hold data of same type and we can decide what type of data that collections can hold.
Some advantages of generic collections - Type Safe, Secure, reduced overhead of type conversions.
So it includes overhead of type conversions.
Generic collections - These are the collections that can hold data of same type and we can decide what type of data that collections can hold.
Some advantages of generic collections - Type Safe, Secure, reduced overhead of type conversions.
// Generic collection
List<T> list = new List<T>();
list.Add("Any object");
// Non generic collection
List list = new List();
list.Add("Any object");
List<T> list = new List<T>();
list.Add("Any object");
// Non generic collection
List list = new List();
list.Add("Any object");
Insight Newgen
Note: All this data has been copied from various sources for the purpose of knowledge sharing. Data content can be either as it is or with little modification.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. What is store procedures
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. What is store procedures
set of Structured Query Language (SQL) statements that perform particular task.SP increase the security to application, it protect from Sql injection and hacking.
Stored procedure have two types of parameters.
a) Output Type Parameter
b) Input Type Parameter.
In SQL we are having different types of stored procedures are therea) System Stored Proceduresb) User Defined Stored procedures
*************************
SP may return one or more values through parameters or may not return at all.SP can return multiple values (max 1024).We can use try catch statements in stored procedures.
Disadvantages:
•Lack of portability. Stored procedures are not portable from one brand of database to another. For example, SQL Server and Sybase cannot run stored procedures created for Oracle, and Oracle cannot run stored procedures created for SQL Server or Sybase.
•Potential for reduced performance. Overburdening the server with stored procedure processing, in addition to standard RDBMS tasks, may degrade database performance.
•Difficult debugging. Nested stored procedures (stored procedures called by other stored procedures) are difficult to debug. Stored procedures invoked from event‑driven triggers are even more difficult to debug.
•Reduced stability. If a stored procedure that was installed as an external DLL and run within the address space of the database engine fails, the server may also fail.
*********************************
*********************************
2. What are generics?
Generics refers to a technique of writing a class without specifying the data type that the class works with. Your code can then declare an instance of such a class and specify the data type. This allows generics classes to be used with many different data types without needing to be rewritten.
******************************
Generics allow you to delay the specification of the data type of programming elements in a class or a method, until it is actually used in the program. In other words, generics allow you to write a class or method that can work with any data type.You write the specifications for the class or the method, with substitute parameters for data types. When the compiler encounters a constructor for the class or a function call for the method, it generates code to handle the specific data type
******************************
Generics allow you to delay the specification of the data type of programming elements in a class or a method, until it is actually used in the program. In other words, generics allow you to write a class or method that can work with any data type.You write the specifications for the class or the method, with substitute parameters for data types. When the compiler encounters a constructor for the class or a function call for the method, it generates code to handle the specific data type
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Generic<string> g = new Generic<string>();
g.Field = "A string";
//...
Console.WriteLine("Generic.Field = \"{0}\"", g.Field);
Console.WriteLine("Generic.Field.GetType() = {0}", g.Field.GetType().FullName);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
public class Generic<T>
{
public T Field;
}
******************************
A collection is simply a collection of whatever. Object, strings, integers, Persons, all of the above...Collections can hold different data type. Here all the elements are objects. In generics, we can specify which datatype we want to store.That might still not be very simple. But basically a 'Generic' is a method to make something work with ANY type. The pro's to this are, as already mentioned, that you avoid 'boxing' and 'unboxing' and that your classes are type-safe.With Generics this is a lot easier. We have collections containing only strings, only integers, only your own custom class type. This, of course, makes it type-safe. We'll never try to cast a string to an integer ever again, because we know the collection contains only strings and not integers.Non-Generic collection which collection can hold the different type of data.Generic collection which collection can hold the same type of data.Generics involves type-safety.Most collection classes derive from the interfaces ICollection, IComparer, IEnumerable, IList, IDictionary, and IDictionaryEnumerator and their generic equivalents.
{
Generic<string> g = new Generic<string>();
g.Field = "A string";
//...
Console.WriteLine("Generic.Field = \"{0}\"", g.Field);
Console.WriteLine("Generic.Field.GetType() = {0}", g.Field.GetType().FullName);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
public class Generic<T>
{
public T Field;
}
******************************
A collection is simply a collection of whatever. Object, strings, integers, Persons, all of the above...Collections can hold different data type. Here all the elements are objects. In generics, we can specify which datatype we want to store.That might still not be very simple. But basically a 'Generic' is a method to make something work with ANY type. The pro's to this are, as already mentioned, that you avoid 'boxing' and 'unboxing' and that your classes are type-safe.With Generics this is a lot easier. We have collections containing only strings, only integers, only your own custom class type. This, of course, makes it type-safe. We'll never try to cast a string to an integer ever again, because we know the collection contains only strings and not integers.Non-Generic collection which collection can hold the different type of data.Generic collection which collection can hold the same type of data.Generics involves type-safety.Most collection classes derive from the interfaces ICollection, IComparer, IEnumerable, IList, IDictionary, and IDictionaryEnumerator and their generic equivalents.
******************************************
3. What is the difference between generics and collections?
Generics provides the type safe code with re-usability like as algorithm. In algorithms such as sorting, searching, comparing etc. you don’t specify what data type(s) the algorithm operates on. The algorithm can be operates with any types of data. In the same way Generics operate, you can provide different data type to Generics. For example, a sorting algorithm can operates on integer type, decimal type, string type, DateTime type etc.
*****************
Code Re-usability with Generics
They simply complement each other, as Collections can exist without Generics and Generics can exist without Collections.
***********************
we have two type of collection:
****************************
With help of Generics you can avoid boxing and unboxing problems.
Generics provides the type safe code with re-usability like as algorithm. In algorithms such as sorting, searching, comparing etc. you don’t specify what data type(s) the algorithm operates on. The algorithm can be operates with any types of data. In the same way Generics operate, you can provide different data type to Generics. For example, a sorting algorithm can operates on integer type, decimal type, string type, DateTime type etc.
*****************
Code Re-usability with Generics
Suppose, you required to sort the integer and floating type numbers, then let's see how to do in collections and generics.
How to do it using Collections
//Overloaded sort methods
private int[] Sort(int[] inputArray)
{
//Sort array
//and return sorted array
return inputArray;
}
private float[] Sort(float[] inputArray)
{
//Sort array
//and return sorted array
return inputArray;
}
How to do it using Generics
private T[] Sort(T[] inputArray)
{
//Sort array
//and return sorted array
return inputArray;
}
*********************They simply complement each other, as Collections can exist without Generics and Generics can exist without Collections.
***********************
we have two type of collection:
****************************
With help of Generics you can avoid boxing and unboxing problems.
4. Can we use return keyword inside a finally block?
No.
you can not leave the body of finally clause like this.
No.
you can not leave the body of finally clause like this.
5. ----Reverse string program without using .net methods?
6. What is caching? And different type of caching?
6. What is caching? And different type of caching?
7. What is boxing and un-boxing? Give example.
Converting a value type to reference type is called Boxing.
Unboxing is the opposite operation and is an explicit operation.
.NET provides a unified type system. All types including value types derive from the type object. It is possible to call object methods on any value, even values of primitive types such as int.
class Test
{
static void Main() {
int i = 1;
object o = i; // boxing
int j = (int) o; // unboxing
}
}
it is ability to treat value types as objects bridges the gap between value types and reference types that exists in most languages
Converting a value type to reference type is called Boxing.
Unboxing is the opposite operation and is an explicit operation.
.NET provides a unified type system. All types including value types derive from the type object. It is possible to call object methods on any value, even values of primitive types such as int.
class Test
{
static void Main() {
int i = 1;
object o = i; // boxing
int j = (int) o; // unboxing
}
}
it is ability to treat value types as objects bridges the gap between value types and reference types that exists in most languages
8. What is the difference between ArrayList and Array?
9. What is indexer?
10. What is cluster and non-cluster index? How many non-cluster index a table can have?
1 Clustered Index + 999 Nonclustered Index = 1000 Index
1 Clustered Index + 999 Nonclustered Index = 1000 Index
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




